Mombasa is a coastal city in Kenya’s Southern Coastal region, bordering Kilifi County to the North, Kwale County to the Southwest, and the Indian Ocean to the East. It serves as the county’s headquarters and hosts several tourist attractions, including the UNESCO World Heritage site Fort Jesus Museum. The city has a cosmopolitan population, predominantly Swahili and Mijikenda, with other communities including Akamba, Taita Bantus, Luo, Luhya, Gusii, and Kikuyu. Mombasa County is an island connected to the mainland through bridges and ferries and has an important Standard-Gauge Railway (SGR) connecting the city to Nairobi City. The Moi International airport is essential for tourism promotion and investment opportunities in the coastal region.
Administrative Units:
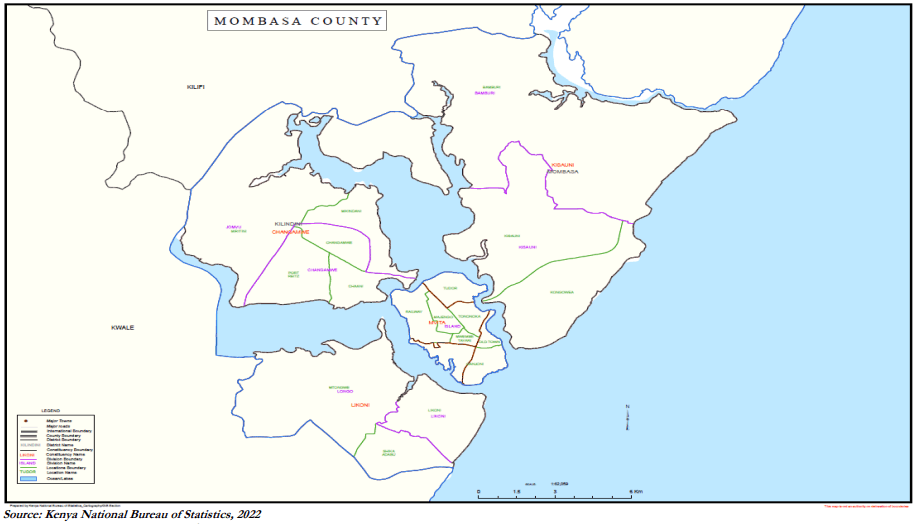
Administratively, the County is divided into six sub-counties namely: Mvita, Nyali, Changamwe, Jomvu, Kisauni, and Likoni and thirty county assembly wards.
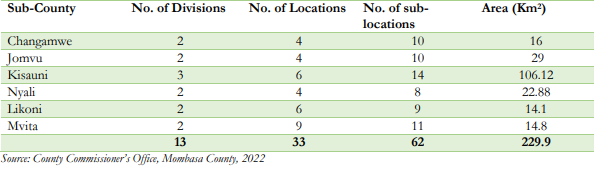
The sub-counties are further sub-divided into thirteen (13) divisions, thirty-three (33) locations and sixtytwo (62) sub-locations with area coverage as shown in the Table.
Population Size and Composition
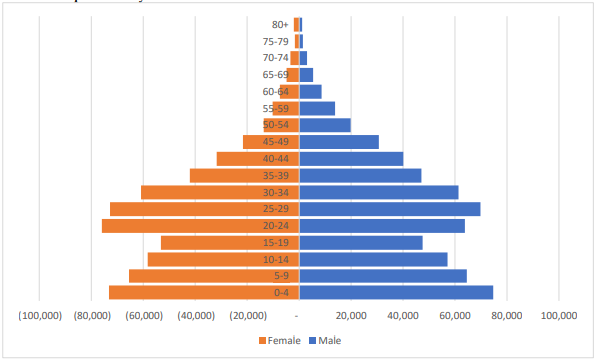
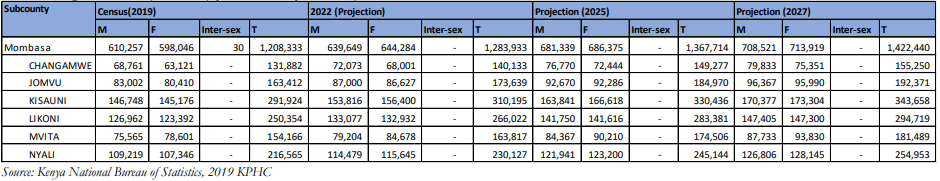
Population distribution and settlement patterns in the County are influenced by proximity to vital social and physical infrastructure networks such as roads, housing, water and electricity. Other factors that influence settlement patterns include accessibility to employment opportunities and security. Table 4 shows the county population projection by sex and age groups. The county’s population, based on the 2019 Kenya Population and Housing Census was 1,208,333 persons of which 610,257 were male and 598,046, were female. The population is projected to reach 1,422,440 by 2027. The most populated sub-county is Kisauni, with a 24% population growth due to low-cost housing and strong land tenure. Changamwe has the lowest population due to poor social infrastructure.
Population Projections (by Sub-County and Sex)
Economy
The main economic activities in the county include Tourism, fishing, mining, agriculture, industrialization, and trade among other activities undertaken in a small scale. It is second to Nairobi in terms of economy.
County Health Facilities
The county has a total of 384 health facilities as per Kenya Master Health facility in 2023. This includes: 64 Public, 291 Private, 17 Faith-based and 12 non-governmental facilities. The sub-county distribution of health facilities is as presented below.
| Sub County | MOH | FBO | PRIVATE | NGO |
| Changamwe | 7 | 2 | 32 | 3 |
| Jomvu | 7 | 4 | 22 | 1 |
| Mvita | 23 | 6 | 78 | 3 |
| Kisauni | 10 | 0 | 60 | 3 |
| Nyali | 8 | 2 | 53 | 2 |
| Likoni | 9 | 3 | 46 | 0 |
| Total | 64 | 17 | 291 | 12 |
Community Units
The County has 253 Community units of which 68% are fully functional. The distribution per sub- county is as shown below:
| Sub County | CHU Registered | Semi Functional | Non- Functional | Closed | Fully Functional | % Full-Functionality |
| Changamwe | 37 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 31 | 84% |
| Jomvu | 33 | 18 | 0 | 1 | 14 | 42% |
| Mvita | 43 | 21 | 0 | 0 | 22 | 51% |
| Kisauni | 39 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 39 | 100% |
| Nyali | 43 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 32 | 74% |
| Likoni | 58 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 33 | 57% |
| Total | 253 | 80 | 0 | 2 | 171 | 68% |
DESIP Project Interventions & Achievements
The DESIP program supports FP Service delivery, demand generation and county coordination. The target audience is WRA, adolescents, poor women and people living with disabilities. The program scope is within 79 health facilities; MOH, Private and Faith Based Facilities.

